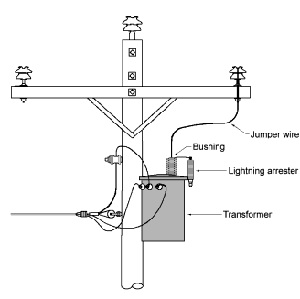
The purpose of the arrester is to limit over-voltages that can appear on the transformer and other electrical devices either due to lightning or other electrical pressure. Base of the top of thearrester is connected to wires or terminals that must beprotected, and the base of the bottom connected to the ground.
Arrester insulation coordination is key in an electric powersystem. When the lightning came into the substation, arresterswork release electric charge (discharge), as well as reducing the voltage to be abnormal about the equipment in the substation.After a lightning arrester is released through, the current is stillflowing because of the system voltage; currents are calleddynamic or current flow aftershocks. Arresters must havesufficient resilience against the flow of energy from theseaftershocks, and should be able to decide, if at the time ofrelease arresters, voltage and current dynamic system is toohigh, then the arrester it may not be able to decide the flow ofaftershocks.
Requirements to be met by the arresters are as follows:1. Voltage spark (sparkover voltage) and the release voltage (discharge voltage), ie the voltage at the terminal at the time of the release should be quite low, so as to secure the insulating equipment. Spark voltage is also called the drain voltage between (gap breakdown voltage). Discharge voltage is also called residual stress (residual voltage) or IR voltage drop.2. Arresters should be able to decide the flow dynamics and can work continues as before. Limits of voltage current system in which the termination of these aftershocks are still possible, called the base voltage (rated voltage) of the arrester
0 comments:
Post a Comment